
In recent years, much of the work done to develop reliable design methods for distillation equipment has been carried out by a commercial organization, Fractionation Research, Inc. A good understanding of methods used for correlating vapor-liquid equilibrium data is essential to the understanding of distillation and other equilibriumstaged processes this subject was covered in Chapter 4. Distillation is probably the most widely used separation process in the chemical and allied industries its applications range from the rectification of alcohol, which has been practiced since antiquity, to the fractionation of crude oil. Only a brief review of the fundamental principles that underlie the design procedures will be given a fuller discussion can be found in Richardson, Harker, and Backhurst (2002), and in other textbooks: King (1980), Hengstebeck (1976), Kister (1992), Doherty and Malone (2001), and Luyben (2006). Though the emphasis is on distillation processes, the basic construction features, and many of the design methods, also apply to other multistage processes, such as stripping, absorption, and extraction.
DEPRIESTER CHART WITH N PROPANOL HOW TO
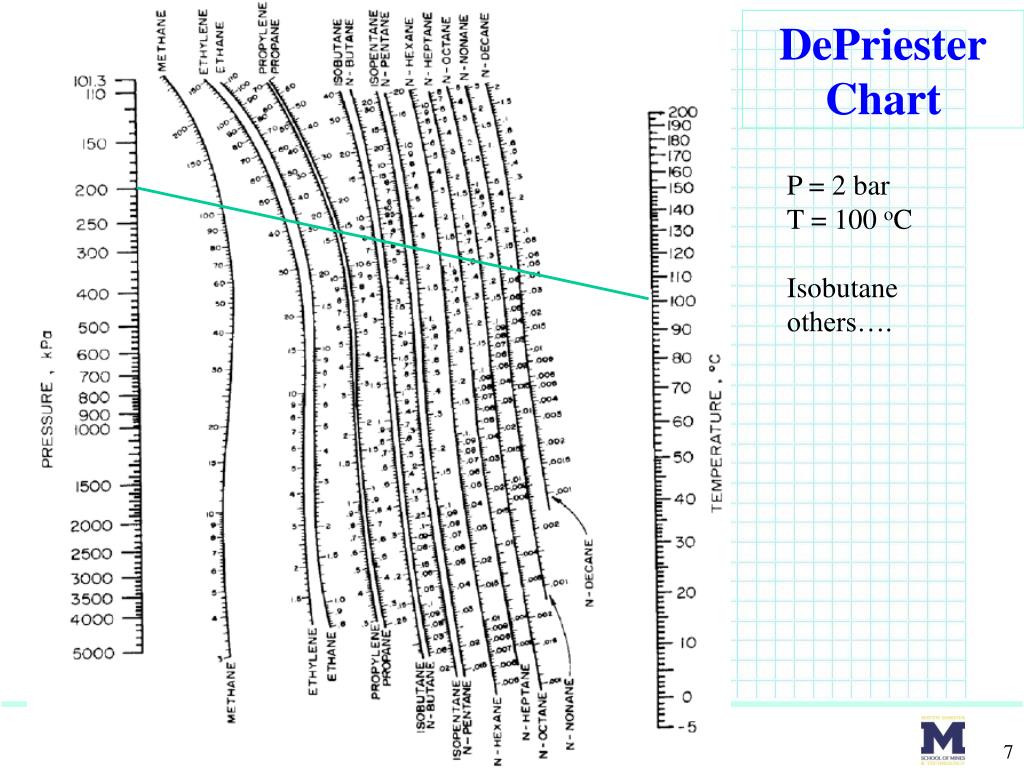
How to design liquid-liquid extraction columnsġ7.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter covers the design of separating columns.How to design absorption and stripping columns.How to design distillation columns using packing instead of trays.How to size distillation columns and select and design distillation column trays.Sequential solution Simultaneous solution Multicomponent FlashĢ9 Binary Flash Overall mole balance mole balance on a mole balance on bģ0 Binary Flash Flash separation: Specify: Find: a = n-pentaneī = n-hexane Vfrac 0.471 V/F P 3.000 bar function -1.89E-08 Xa 0.394 Xb 0.606 Ya 0.619 Yb 0.Separation Columns (Distillation, Absorption, and Extraction) P = bar T = various oC Benzene - Toluene Y vs X diagram T vs X or Temp vs CompositionĢ6 Effect of Pressure: Seader & Henley (2006)Ģ8 Overview Brief thermodynamics review Binary Flash with energy balance Mixtures to model: MeOH – water EtOH – water propanol – water n-butanol – water n-butane – n-pentane benzene – toluene acetic acid – propionic acid CO2 – toluene (high P) Vapor phase: good liquid phase: good for HC or moderate – high pressures (compressible liquid phase) Typically used for liquid phase fugacity calculations Used for special cases (like gases dissolving into liquid phase) Equations of state models Activity coefficient modelsġ7 Overview Introduction UO course overview Equilibrium Stage separations Historically, when estimates were done by hand: Sometimes the K values are nearly composition independent “hand” techniques of design/solution have used DePriester Charts (hydrocarbons):ħ DePriester Chart P = 2 bar T = 100 oC Isobutane others….

Historically, when estimates were done by hand: Seader & Henley (2006)
Vapor phase: good liquid phase: good for HC or moderate – high pressures (compressible liquid phase) Typically used for liquid phase fugacity calculations Used for special cases (like gases dissolving into liquid phase) Typical simplifications: Ideal vapor phase Ideal liquid phase Raoult’s Law What are “Unit Operations” Brief thermodynamics review Binary flash with energy balance Multicomponent flash 2 Overview Introduction UO course overview Equilibrium Stage separations


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
